|
The Definition of Macular Degeneration
When we talk about the Definition of Macular Degeneration we have to include many things. Myths: Everyone with macular degeneration is going to continue losing vision, and there is no effective treatment to avoid this. Facts: You do not have to lose your vision with
Macular Degeneration
There are steps you can take to stabilize and even possibly Improve your Vision. Certain nutrients such as omega-3 fish oil and CoQ10 with L-Carnitine may help slow down macular degeneration and preserve vision. Lifestyle changes may also help. Some research indicates that daily use of Microcurrent Stimulation may help preserve vision as well. Overview:
The Definition of Macular Degeneration (ARMD-Aged Related Macular Degeneration) is the slow deterioration of the cells in the macula, a tiny yellowish area near the center of The Retina where vision is the most precise. This deterioration therefore affects your central vision, the very vision you use for reading, writing, driving and recognizing faces. ARMD causes the loss of central vision. Your peripheral vision is not affected. There are two types of macular degeneration: Ninety percent of people with macular degeneration have the dry type, in which small, yellow spots called drusens form underneath the macular. Drusens are believed to be waste products that accumulate because of lack of antioxidants to clear the waste from the eyes. The drusen slowly break down the cells in the macular, causing distorted vision. Dry Macular Degeneration can progress to the second, more severe type, called wet Macular Degeneration. In the wet type, new, abnormal blood vessels begin to grow toward the macular, causing rapid and severe vision loss.
Also see the
Amsler Test Grid & Instructions for a self - test
and a definition of Macular Degeneration.
Causes:
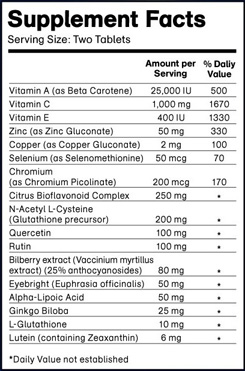
Free radicals are also natural byproducts of metabolism. These highly reactive chemicals cause oxidation, and can destabilize healthy cells in the back of the eyes. Free radical damage is accelerated by smoking, chronic fatigue and compromised immune systems. Nutritional Deficiencies and Poor Digestion - Often sufferers of Macular Degeneration are deficient in some or many of the important nutrients including essential fatty acids, lutein, zeaxanthin, taurine, antioxidants, bioflavenoids, zinc, selenium, vitamin B-complex.

Subscribe to EyeSight Vision Care! , our monthly newsletter with in depth information to help you keep up to date on how to Protect Your Eyesight with a free bonus. Fill out the form below. You'll then receive an email asking you to confirm that you subscribed. You'll always have the option to unsubscribe at the click of your mouse.
Definition of Macular Degeneration to Macular Degeneration Symptoms
|
More Information